WHAT ARE DAOs?

INTRODUCTION
If you're like most people, you've probably been hearing a lot about DAOs lately. You know, those things that are apparently the "next big trend" in the crypto world? DAOs have been around for a while now, but they've only recently started to gain mainstream attention. So what are DAOs, and why should you care? In this article, we'll discuss DAOs in detail and explore why they're such an important innovation in the crypto world. We'll also take a look at some of the real-world applications of DAOs and how they're changing the way we do business.
WHAT ARE DAOs?
DAOs (or Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) are organizations that are run entirely on blockchain technology. DAOs are decentralized, meaning there is no central authority controlling them. They're also autonomous, meaning that they operate without any human intervention. All decisions about the DAO are made by its members using voting or other consensus mechanisms the DAO specifically applies.
The first DAO was created in 2016 by Slock.it and it was known as The DAO. The DAO was a venture capital fund that raised over $150 million through a crowd-sale. However, The DAO was hacked in June of 2016 and lost over $50 million worth of ethers (the currency of Ethereum). This incident led to the creation of Ethereum Classic, a separate cryptocurrency that is based on the original Ethereum blockchain.
5 years after The DAO fiasco, DAOs have become much more popular and there are now dozens of them in existence. DAOs aren't just some theoretical concept - they're already being used in the real world and can be used for a variety of purposes, including fundraising, governance, project management, and more.
HOW DOES A DAO WORK?
Although the concept of DAOs seems like something out of science fiction, they actually work quite similarly to traditional organizations. The difference between a regular organization versus a DAO is that DAOs do not have any stable governance hierarchy with rules from “above” stating what can be done and who gets to make decisions (meaning they are decentralized). Instead, people vote on different proposals in order for those policies or ideas to come into existence - similar if we think about voting in larger societies when individuals get together and decide amongst themselves in which direction they want their economy/society/community to go.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF DAOs?
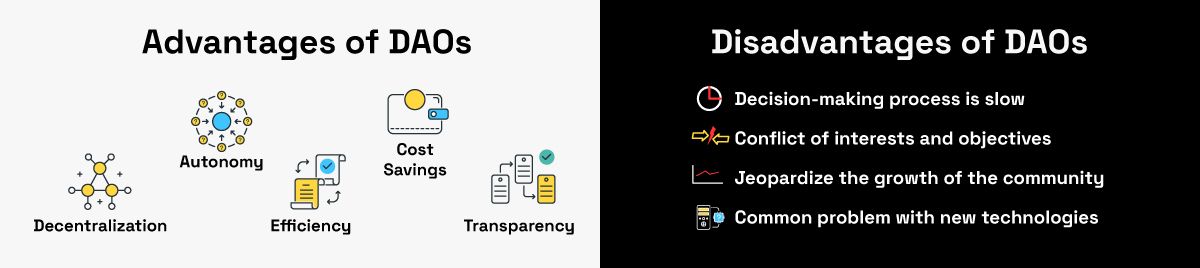
There are several advantages to using DAOs:
- Decentralization: As mentioned earlier, DAOs are decentralized, meaning there is no central authority controlling them. This makes them more secure and less vulnerable to attack. It also eliminates the need for a middleman or centralized authority figure.
- Autonomy: DAOs are autonomous, meaning they operate without any human intervention. All decisions about the DAO are made by its members using voting or consensus mechanisms. This allows for greater flexibility and faster decision making.
- Transparency: Because all transactions on the blockchain are public, DAOs are transparent and accountable. This makes them more trustworthy and less prone to corruption.
- Efficiency: DAOs are more efficient than traditional organizations because they don't require a lot of bureaucracy or red tape. All decisions are made quickly and efficiently by the members of the DAO.
- Cost Savings: DAOs can save businesses money by eliminating the need for middlemen or centralized authorities. This reduces costs and allows businesses to operate more cheaply and efficiently.
WHAT ARE THE DISADVANTAGES OF DAOs
Despite the potential benefits of DAOs, there are also several drawbacks to this technology. Some of these pitfalls include:
1. The decision-making process is slow due to voting. Every member has to vote before the final decision can be agreed on.
2. There might be conflict of interests and objectives among members, which can get as bad as some members breaking out to create another platform. For example, Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash.
3. Some communities might have members that do not have good understanding about governance and votes from such members might jeopardize the growth of the community.
4. The common problem with new technologies is the probable regulations and legal issues that no one can be sure of, which can put investors/members in uncertain situations.
THE ECONOMY OF DAOs
Like all cryptocurrencies, DAO tokens (the currency of DAOs) are created through mining. Miners are rewarded with DAO tokens for verifying transactions on the blockchain. The value of DAOs is determined by supply and demand on cryptocurrency exchanges.
As DAOs become more popular, the value of DAO tokens is likely to increase. This makes DAOs an attractive investment opportunity and could lead to a DAO bubble similar to the one we saw with Bitcoin in 2017.
WHAT ARE THE REAL - WORLD APPLICATIONS OF DAOs

DAOs have a variety of real-world applications, including:
• Fundraising: DAOs can be used for crowdfunding campaigns and raising money from investors.
• Governance: DAOs can be used for governance purposes, such as voting on important decisions or electing board members.
• Project Management: DAOs can be used for project management, allowing team members to collaborate and track progress.
• Marketing: DAOS can be used for marketing campaigns, allowing businesses to reach a wider audience.
• Recruitment: DAOs can be used for recruiting new employees, allowing businesses to find the best candidates for the job.
ECOSYSTEM AND ADOPTION
The DAO ecosystem is still relatively young and it's still undergoing development. However, there are already a number of projects that are using DAOs to power their businesses. Some notable examples include:
Aragon: A decentralized governance platform that allows organizations to operate without any central authority. The network software offers Aragon Client, Aragon Network and Aragon Association. It is governed by ANT token holders.
Colony: A platform for building decentralized companies. It provides everything an organisation needs to function on-chain. After creating a DAO, there’s a need to manage other operational phases. Colony solves these problems in all.
The DAO: designed to allow users to send money from anywhere in the world anonymously. The absence of a central authority meant reduction in costs and more controlling power for the investors. Though the hack into The DAO system in 2016 marked the beginning of the end for it, different blockchain projects have looked into the framework for inspiration on what to model and what to improve on.
Ethereum Classic: it allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts. After The DAO’s hack in 2016, the Ethereum network had to split into two different blockchains (Ethereum and Ethereum classic) in a bid to erase the The DAO hack from the Ethereum blockchain history. ETC (the operational token of Ethereum classic) gives holders the ability to vote on a variety of issues and statements.
MakerDAO: is governed by a community of MKR token holders and uses DAOs to manage DAI stable coins. It was built to facilitate the lending and borrowing of cryptocurrencies without a third party. To take out a loan (that would be paid in DAI) you will need to deposit a cryptocurrency like ETH as collateral which should be more than the amount of DAI you want to receive. Your collateral will be liquidated through an auction if it drops below the value of DAI loaned.
DAOstack: a platform designed for managing and creating DAOs. The toolkit was designed to enable easy linking of new DAOs with pre-existing ones with its high scalability.
Uniswap DAO: this is a decentralized exchange(DEX) platform offering peer-to-peer trading of different token pairs. UNI (Uniswap’s governance token) has the largest market cap among the DAO tokens. Holders of this token can vote for protocol changes and “delegate” tokens to others. To propose protocol changes, you need to have at least 10 million UNI, either yours or delegated to you.
Compound DAO: this is a Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platform that supports 18 different tokens including ETH and TETHER. Just like MakersDAO, when you deposit a crypto into the Compound pool, you will get the equivalent value in cTokens(cTETHER if you deposited TETHER). Your cTokens exchange rate increases over a period and earns you an interest when you want to withdraw eventually. The COMP token is the governing token of the organization. You must have at least 65,000 COMP tokens before your proposed changes can be voted on.
BanklessDAO: this started off as an email newsletter teaching crypto-enthusiasts the concept of Decentralized Finance (DeFi). The BanklessDAO launched last year and aims to liberate people from centralized traditional banking systems. BANK is the community’s governance token, which can be earned by your contribution to the DAO.
Audius: this is an ethereum-based and community-owned streaming platform. Think of a platform like Spotify, but without a centralized authority. The aim of the creators is to provide artists with more control over their music and not record labels. It is free to use for both artists and listeners. The community is governed by AUDIO token holders that can vote and propose changes.
The number of DAO projects is growing every day and it's likely that we'll see even more impressive applications in the near future.

